Introduction
Welcome to the world of Association Rules and Apriori Algorithm! If you’re in the business analytics field, then you must have heard about these terms. But if you’re new to this, then let’s start with the basics. Association Rules are a type of rule-based machine learning technique used to establish relationships between variables in a dataset. The purpose of Association Rules and Apriori Algorithm is to identify patterns and correlations among various items or products and suggest opportunities for better revenue generation. Okay, we know this sounds like a lot of technical jargon in one go. But don’t worry, we’re here to make it fun and interactive for you. So hold on to your chairs, and let’s dive deep into the ocean of Association Rules and Apriori Algorithm!
Understanding Association Rule Mining
Understanding Association Rule Mining Association Rule Mining is a technique used in data mining to identify patterns and relationships in a large dataset. The main purpose is to find relationships between different items, and the strength of these relationships is determined by metrics such as support, confidence, and lift. For instance, consider a supermarket where you shop frequently. The supermarket would like to determine items that are commonly bought together so that they can place these items near each other in the store, thus optimizing their sales. The association rule may tell the supermarket that a customer who buys bread is likely to buy butter as well. The Apriori algorithm is often used to generate associations, as it is efficient and straightforward. Support indicates the frequency of items appearing together, confidence indicates the probability of one item being bought given the other one is bought, and the lift shows whether the two items are independent or correlated. The importance of association rule mining cannot be overstated, as it can reveal valuable information about customer behavior and the relationships between different products.
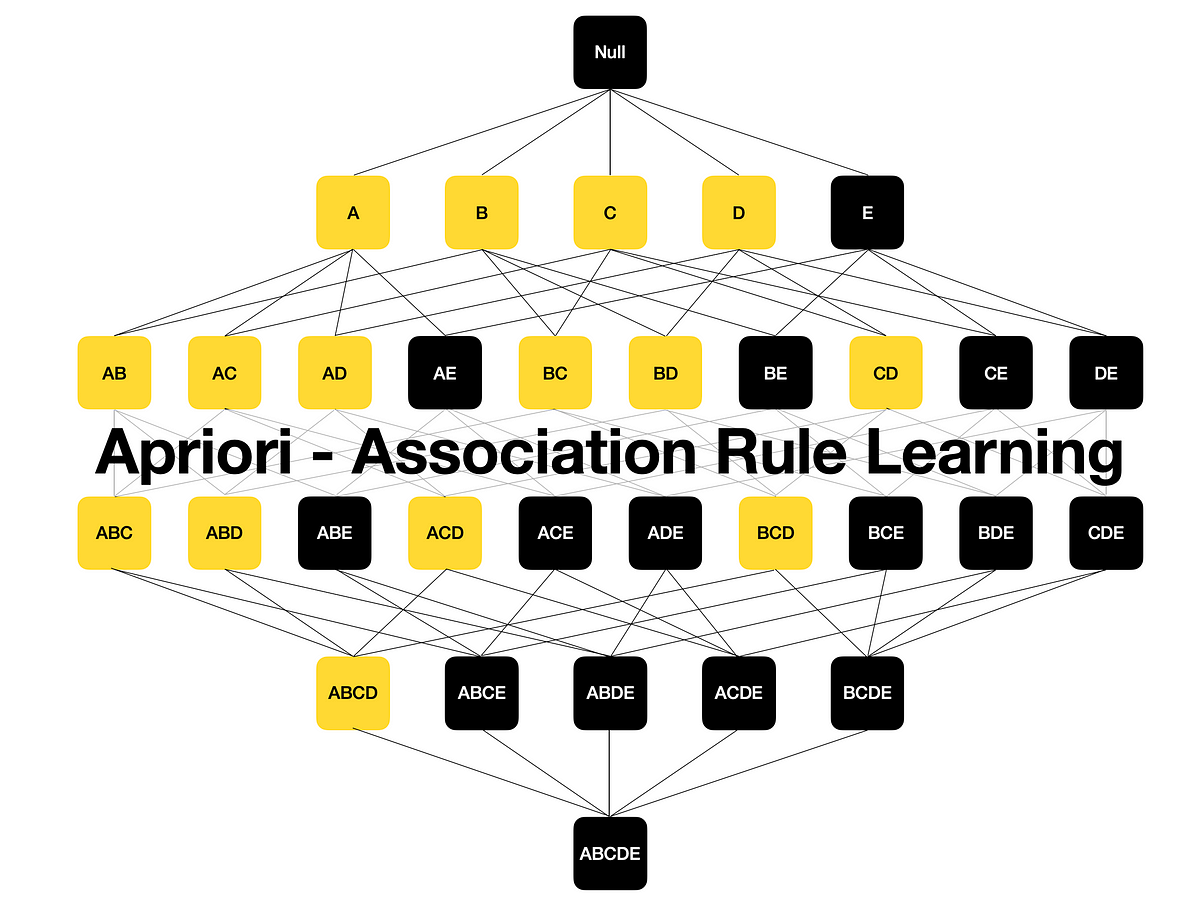
Apriori Algorithm
So now that we have gone over what Association Rules are and why they’re useful, it’s time to dive into the Apriori Algorithm. Brace yourselves, because we’re going to get technical. The Apriori Algorithm is a popular algorithm used in Data Mining for Association Rule Learning. In simpler terms, it helps identify the correlation between items in a dataset. And how does it do that, you ask? Well, let me tell you. The algorithm works by creating a frequent itemset, which is basically a set of items that frequently occur together in the dataset. The frequent itemsets are then used to generate association rules, which are essentially if-then statements that show the relationship between the items. Now, let’s break down the steps involved in the Apriori Algorithm. First, we set a minimum support threshold, which is the minimum number of times an itemset needs to occur in the dataset to be considered frequent. Then, we generate all the frequent itemsets of length 1. We use these frequent itemsets to generate frequent itemsets of length 2, and so on until we can no longer generate any more frequent itemsets. One of the main advantages of using the Apriori Algorithm is that it’s easy to understand and implement. Another advantage is that it’s widely used in industry and has plenty of documentation available. However, there are some disadvantages to using the Apriori Algorithm as well. For example, it can be computationally expensive and inefficient when dealing with large datasets. But fear not, there are ways to improve the efficiency of the Apriori Algorithm. One such way is to use the FP-Growth Algorithm, which we’ll touch on in the next section. Now that you have a good understanding of the Apriori Algorithm, it’s time to put it into practice with some real-world examples. But before we do that, let’s quickly summarize what we’ve learned about the algorithm so far: -The Apriori Algorithm is used for Association Rule Learning. -It works by generating frequent itemsets and association rules. -The main advantage of using the Apriori Algorithm is its ease of use and availability of documentation. -Some disadvantages include its inefficiency with large datasets. Stay tuned for the next section where we will implement the Apriori Algorithm on a real dataset.
Implementing Apriori Algorithm with Real-world examples of time, especially when there are millions of transactions to evaluate. As a result, we often reach a point where the algorithm fails to generate any association rules, which is frustrating. Fear not, for we have an efficient solution – the FP-Growth algorithm! It drastically reduces the time taken to generate association rules and is ideal for large datasets. The FP-Growth algorithm also makes it easy to modify the minimum support threshold, making it a great alternative to the Apriori algorithm. With the FP-Growth algorithm, dealing with big data becomes a breeze!
Support
Support (relative support) is the proportion of transactions containing a certain item set. An item set can contain more than one item.
Say the item set Fruit contains apple and banana, and our database looks like this.

The support of Fruit is 1/4 (=0.25) since only 1 out of 4 transactions (the 1st transaction) contains apple and banana.
Confidence
As you might imagine, we need some measures to evaluate the association rules. Support measures the frequency of item sets co-occurring in a rule, and Confidence is a reliability measure of a rule. In specific, support of a rule A → B is the support of the union of A and B, which is the proportion of transactions that contain both A and B. Confidence is the proportion of transactions containing A also contains B. If the confidence is high, we know the rule is applicable to our database, we should hence further investigate the rule.
Using the same example above, what’s the support and the confidence of rule (Apple) → (Banana)?
The support of Apple is 1/4 since 1 out of 4 transactions contains apple, and the support of Apple and Banana is also 1/4 as we mentioned before. Thus, the support of this rule is 1/4, and the confidence is 1/4 divided by 1/4, which is 1!
Now let’s think about the support and the confidence of rule (Banana) → (Apple).
The support of Banana is 3/4 since 3 out of 4 transactions contains banana, and the support of Apple and Banana is 1/4. Therefore, the support of this rule is 1/4, and confidence is 1/4 divided by 3/4, which is 1/3! The support of rule A → B is the same as the rule B → A, but the confidence of them is often different!
Lift
Lift is a measure of how much more often two items occur together than expected if they were statistically independent. In other words, it measures the strength of association between two items. A lift of 1 indicates that the items are independent, while a lift greater than 1 indicates a positive association between the items, and a lift less than 1 indicates a negative association.

Conclusion
Congratulations on making it to the end of this comprehensive guide on Association Rules and the Apriori Algorithm! Now that you have an understanding of the importance of Association Rules and the Apriori Algorithm in Business Analytics, let’s discuss the future scope and applications. The potential applications of Association Rules and the Apriori Algorithm are vast, from market basket analysis to customer segmentation to recommendation engines. As the amount of data generated by businesses and consumers increase, the need for efficient and effective data mining techniques will continue to grow. Moreover, the future scope of Association Rules and the Apriori Algorithm is not limited to just Business Analytics. The healthcare industry can utilize these techniques for medical diagnoses and patient monitoring, while researchers can use it for analyzing scientific data. In conclusion, mastering Association Rules and the Apriori Algorithm can be a game-changer for businesses and industries alike. So, whether you are a data scientist or a business owner, incorporating these techniques in your workflow can lead to valuable insights and drive better decision-making. Thanks for reading!
Implementation of Apriori Algorithm with Real-world examples Now that we have a good understanding of the Apriori Algorithm and the metrics for Association Rules, it’s time to implement the algorithm in the real world and see how it fares. Data Preparation for Apriori Algorithm Before implementing the Apriori Algorithm, we need to prepare the dataset appropriately. The dataset should be in the form of a transactional database with each row representing a transaction and columns representing the items bought. The items should be encoded with numerical values for the algorithm to work correctly. Implementing Apriori Algorithm on Online Retail Dataset Let’s say you work for an online retail company. The marketing team wants to know which products are frequently bought together so that they can create bundled deals. We apply the
To apply the Apriori Algorithm on the online retail dataset, we need to set a support threshold indicating the minimum frequency of items that we want the algorithm to consider for generating Association Rules. Once we set this threshold and input the dataset into the algorithm, we can analyze the output to identify which products customers tend to buy together. This information can help the marketing team create targeted promotions and discounts, increasing customer satisfaction and revenue for the online retail company.